Self-Host Bitwarden: Enterprise Password Management with Complete Data Control
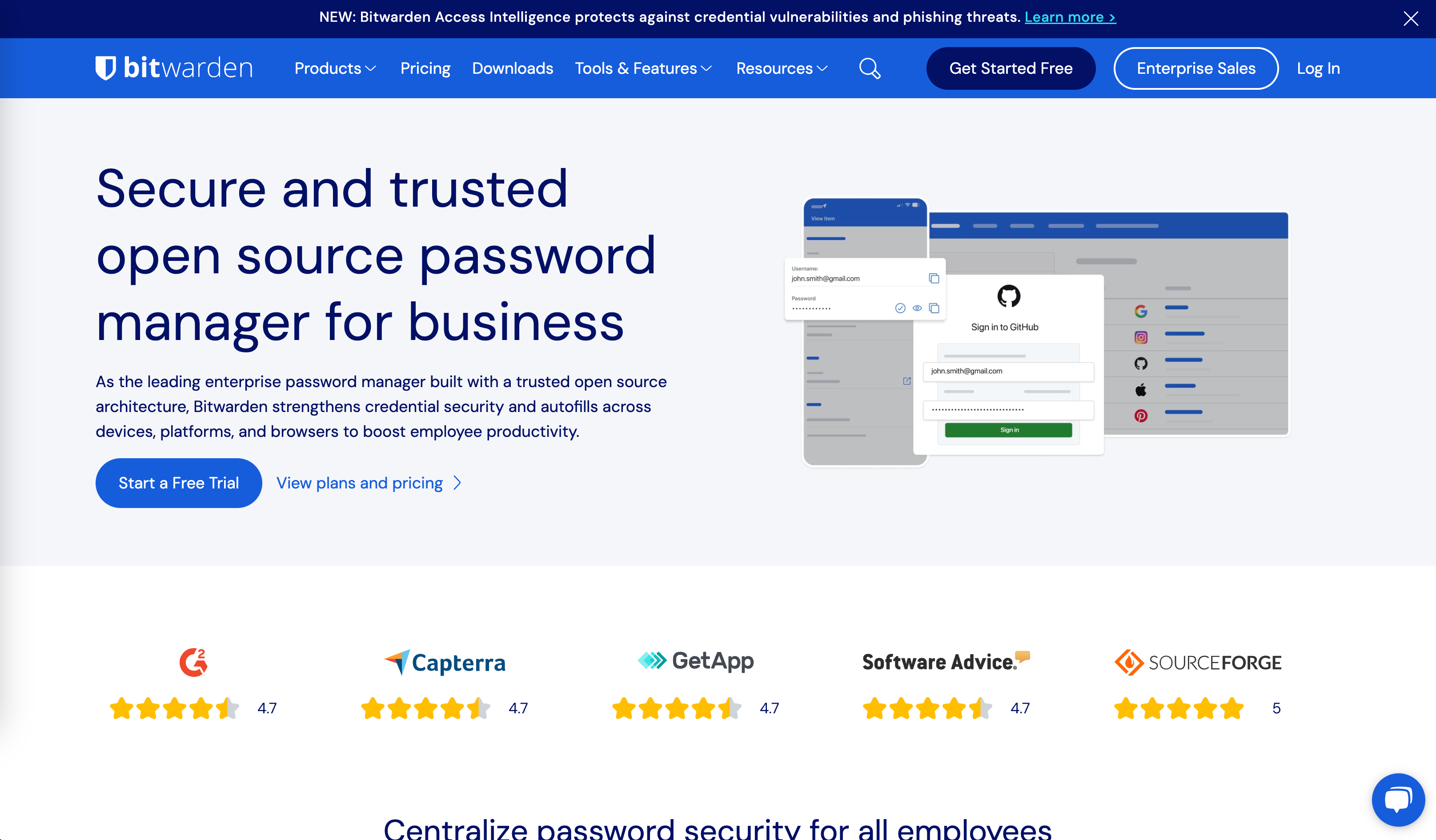
What is Bitwarden Self-Hosting?
Bitwarden Self-Hosting allows you to run the complete Bitwarden password management solution on your own infrastructure, providing enterprise-level security with full data control. This open-source alternative to cloud-based password managers offers the same powerful features as Bitwarden's hosted service while ensuring your sensitive password data never leaves your environment. Perfect for organizations requiring data sovereignty, enhanced privacy, or specific compliance requirements.
Key Features of Self-Hosted Bitwarden
🔐 Enterprise Password Management
- Unlimited Passwords: Store unlimited passwords, secure notes, and sensitive information
- Advanced Encryption: Zero-knowledge end-to-end encryption with client-side data protection
- Cross-Platform Access: Native apps for Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, Android, and web browsers
- Auto-Fill & Generate: Automatic password filling and secure password generation
- Secure Sharing: Encrypted password sharing between team members and organizations
👥 Organization & Team Features
- User Management: Centralized user provisioning and access control
- Collections: Organize passwords by department, project, or access level
- Role-Based Access: Fine-grained permissions for different user roles and responsibilities
- Group Management: Simplified access control through user groups
- Admin Dashboard: Comprehensive administrative interface for user and security management
🛡️ Advanced Security Features
- Two-Factor Authentication: Support for TOTP, email, YubiKey, and FIDO2 authentication
- Security Reports: Identify weak, reused, or compromised passwords across the organization
- Event Logging: Comprehensive audit trails for compliance and security monitoring
- Vault Health: Regular security assessments and password strength analysis
- Emergency Access: Secure emergency password access for trusted contacts
🔧 Self-Hosting Benefits
- Complete Data Control: All password data remains on your infrastructure
- Custom Compliance: Meet specific regulatory requirements and data residency laws
- No External Dependencies: Fully offline-capable password management
- Unlimited Users: No per-user pricing limitations for enterprise deployments
- API Access: Full administrative API for automation and integrations
Why Choose Self-Hosted Bitwarden?
Bitwarden Self-Hosted vs 1Password Business ($8/user/month)
| Feature | Bitwarden Self-Hosted | 1Password Business |
|---|---|---|
| Monthly Cost | Free Core Features | $8/user/month |
| Data Location | ✅ Your Infrastructure | ❌ 1Password Servers |
| User Limits | ✅ Unlimited | ❌ Per-User Pricing |
| Custom Compliance | ✅ Full Control | ❌ Limited Options |
| API Access | ✅ Complete API | ❌ Limited API |
| Offline Access | ✅ Fully Offline | ❌ Requires Internet |
Bitwarden Self-Hosted vs LastPass Enterprise ($4-7/user/month)
- Security Track Record: Open-source transparency vs proprietary security concerns
- Data Ownership: Complete control vs third-party data processing
- Cost Predictability: One-time setup vs ongoing per-user subscriptions
- Feature Access: All features included vs tiered feature restrictions
Bitwarden Self-Hosted vs Bitwarden Cloud
- Data Sovereignty: Your servers vs Bitwarden's cloud infrastructure
- Compliance Control: Custom compliance vs standard cloud compliance
- Performance: Local network speed vs internet-dependent access
- Customization: Self-managed updates vs automatic cloud updates
Quick Deployment Options
Option 1: Official Docker Installation (Recommended)
The officially supported method using Bitwarden's installation script.
# Download and install Bitwarden
curl -Lso bitwarden.sh https://go.btwrdn.co/bw-sh
chmod 700 bitwarden.sh
# Run installation script
./bitwarden.sh install
# Configure your installation
./bitwarden.sh config
# Start Bitwarden services
./bitwarden.sh start
Option 2: Vaultwarden (Lightweight Alternative)
A community-driven Rust implementation compatible with Bitwarden clients.
# Quick Docker deployment
docker run -d \
--name vaultwarden \
-e WEBSOCKET_ENABLED=true \
-v vw-data:/data \
-p 80:80 \
vaultwarden/server:latest
Production Vaultwarden Configuration:
version: '3.8'
services:
vaultwarden:
image: vaultwarden/server:latest
container_name: vaultwarden
restart: unless-stopped
environment:
- WEBSOCKET_ENABLED=true
- SIGNUPS_ALLOWED=false
- ADMIN_TOKEN=your_admin_token
- DOMAIN=https://your-domain.com
- SMTP_HOST=your-smtp-server.com
- SMTP_FROM=admin@your-domain.com
- SMTP_PORT=587
- SMTP_SECURITY=starttls
- SMTP_USERNAME=your-smtp-username
- SMTP_PASSWORD=your-smtp-password
volumes:
- vw_data:/data
ports:
- "80:80"
volumes:
vw_data:
Option 3: Docker Compose Production Setup
Complete production deployment with PostgreSQL and backup automation.
version: '3.8'
services:
bitwarden:
image: bitwarden/self-host:latest
restart: unless-stopped
ports:
- "80:8080"
- "443:8443"
environment:
- BW_DOMAIN=your-domain.com
- BW_DB_PROVIDER=postgresql
- BW_DB_SERVER=postgres
- BW_DB_DATABASE=bitwarden
- BW_DB_USERNAME=bitwarden
- BW_DB_PASSWORD=secure_password
depends_on:
- postgres
volumes:
- bitwarden_data:/etc/bitwarden
- bitwarden_logs:/var/log/bitwarden
postgres:
image: postgres:15
restart: unless-stopped
environment:
- POSTGRES_DB=bitwarden
- POSTGRES_USER=bitwarden
- POSTGRES_PASSWORD=secure_password
volumes:
- postgres_data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
volumes:
bitwarden_data:
bitwarden_logs:
postgres_data:
Getting Started with Self-Hosted Bitwarden
Initial Setup Process
- Server Preparation: Set up a server with Docker and sufficient resources
- Domain Configuration: Point your domain to the server's IP address
- SSL Certificate: Configure HTTPS with Let's Encrypt or custom certificates
- Installation: Run the Bitwarden installation script or deploy Docker containers
- Admin Configuration: Access the admin panel to configure organization settings
Essential Configuration Steps
- SMTP Setup: Configure email settings for user invitations and notifications
- User Registration: Set up the first admin account and create organization
- Security Policies: Configure two-factor authentication and password policies
- Backup Configuration: Set up automated backups for the Bitwarden database
- Client Installation: Deploy Bitwarden clients across user devices
Security Best Practices
- Regular Updates: Keep Bitwarden and underlying systems updated with security patches
- Access Controls: Implement strong authentication and limit administrative access
- Network Security: Use firewalls and VPNs to secure server access
- Backup Encryption: Encrypt backup data and store securely off-site
- Monitoring: Implement logging and monitoring for security events
Popular Use Cases
Small Business Password Management
- Team Collaboration: Securely share passwords and sensitive information
- Client Access: Provide secure access to client credentials and accounts
- Compliance: Meet industry-specific password security requirements
- Cost Control: Avoid per-user subscription costs with self-hosting
Enterprise Security Infrastructure
- Data Sovereignty: Keep sensitive credentials within corporate infrastructure
- Compliance Requirements: Meet GDPR, HIPAA, SOX, and other regulatory standards
- Integration: Connect with existing identity management and security systems
- Custom Policies: Implement organization-specific security policies and procedures
Development Teams
- API Key Management: Securely store and share development credentials
- Environment Secrets: Manage production, staging, and development passwords
- Team Onboarding: Quickly provision access for new team members
- Project Isolation: Organize credentials by project or client engagement
Family & Personal Use
- Family Sharing: Share household passwords and accounts securely
- Legacy Planning: Set up emergency access for family members
- Privacy Control: Keep personal data away from commercial cloud services
- Cost Savings: Avoid subscription fees for family password management
Advanced Features & Management
API Integration
# Create organization user via API
curl -X POST "https://your-bitwarden.com/api/organizations/{orgId}/users/invite" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer your-api-token" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"emails": ["user@example.com"],
"type": 2,
"accessAll": false,
"collections": []
}'
# Get organization vault items
curl -X GET "https://your-bitwarden.com/api/organizations/{orgId}/ciphers" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer your-api-token"
Backup and Disaster Recovery
# Automated backup script
#!/bin/bash
DATE=$(date +%Y%m%d_%H%M%S)
BACKUP_DIR="/backup/bitwarden"
# Create database backup
docker exec bitwarden_postgres pg_dump -U bitwarden bitwarden > $BACKUP_DIR/db_$DATE.sql
# Backup Bitwarden data directory
tar -czf $BACKUP_DIR/data_$DATE.tar.gz /path/to/bitwarden/data
# Encrypt backups
gpg --cipher-algo AES256 --compress-algo 1 --s2k-digest-algo SHA512 \
--symmetric $BACKUP_DIR/db_$DATE.sql
Organization Management
// PowerShell script for bulk user management
$users = Import-Csv "users.csv"
foreach ($user in $users) {
Invoke-RestMethod -Uri "https://your-bitwarden.com/api/organizations/orgId/users/invite" `
-Method POST `
-Headers @{"Authorization"="Bearer $apiToken"; "Content-Type"="application/json"} `
-Body (@{
emails = @($user.Email)
type = 2
accessAll = $false
collections = @()
} | ConvertTo-Json)
}
Bitwarden Community & Support
- GitHub Repository: Multiple repositories for server, clients, and mobile apps
- Community Forum: Active community discussions and support
- Documentation: Comprehensive setup and administration guides
- Regular Updates: Monthly releases with new features and security improvements
- Professional Support: Optional commercial support available for enterprise deployments
Migration & Implementation Guide
From Cloud Password Managers
- Data Export: Export existing password data from current provider
- Bitwarden Setup: Deploy and configure self-hosted Bitwarden instance
- Data Import: Import password data using Bitwarden's import tools
- Client Deployment: Install Bitwarden clients on all user devices
- Training & Adoption: Train users on Bitwarden features and best practices
From Existing Self-Hosted Solutions
- Backup Current System: Create complete backup of existing password data
- Parallel Deployment: Set up Bitwarden alongside existing system
- Data Migration: Convert and import password data to Bitwarden format
- User Testing: Validate all critical passwords and access requirements
- System Cutover: Migrate users to Bitwarden and decommission old system
Secure your organization's digital assets with self-hosted Bitwarden - the enterprise-grade password management solution that puts security and privacy under your complete control.